For media enquiries please contact:
Liz Sharma
Liz@sharmacomms.co.uk / +44 (0)7963 122988
“Sustainable Intensification” of African Agriculture Explained in New Online Database
Policy initiative Agriculture for Impact compiles evidence-based overview and case studies of key approaches to tackling food insecurity in Africa
LONDON – An essential guide to Sustainable Intensification, the practical pathway towards producing more food with less impact on the environment, whilst improving livelihoods and wellbeing is launched today by Agriculture for Impact, a London-based advocacy initiative based at Imperial College London.
The online resource offers policy makers and researchers a balanced and evidence-based breakdown of many agricultural approaches in African agriculture, for example the role of organic agriculture, water conservation, biotechnology, and participatory agricultural research. Case studies and technical briefs for each approach are also covered.
Access the Sustainable Intensification Database at: http://ag4impact.org/database
“Sustainable Intensification must become a new paradigm for African agriculture to capture the dual purpose of intensifying food production while ensuring the natural resource base on which agriculture depends is sustained, and indeed improved, for future generations,” comments Sir Gordon Conway, Director of Agriculture for Impact.
“This database aims to create an evidence base to underpin the complex political and physical dimensions to solving hunger, malnutrition and poverty in Africa through agricultural development. It has concise information and evidence to inform action from policy makers and donors in a rational, impactful way,” he adds.
 The Sustainable Intensification database builds on extensive work by Agriculture for Impact on this approach, in particular in its role as convenor of the Montpellier Panel of experts, which published the influential report “Sustainable Intensification: A New Paradigm for African Agriculture” in 2013. This flagship report was responsible for updating and redefining the concept of Sustainable Intensification, and bringing it onto the global policy agenda for food security in the developing world.
The Sustainable Intensification database builds on extensive work by Agriculture for Impact on this approach, in particular in its role as convenor of the Montpellier Panel of experts, which published the influential report “Sustainable Intensification: A New Paradigm for African Agriculture” in 2013. This flagship report was responsible for updating and redefining the concept of Sustainable Intensification, and bringing it onto the global policy agenda for food security in the developing world.
“Yields have been the dominant aspect of efforts to improve production in recent decades,” comments Emily Alpert, Deputy Director of Agriculture for Impact. “However, given the environment in which we now live, that has an ever expanding population which must be fed in the face of the threats posed by climate change, it is now critically important to place as much emphasis on ‘sustainable’ as we do on ‘intensification’.”
“Conventional intensification is not a viable solution if it comes at the expense of environmental and social resources. We need radical measures and new paradigms. That is what we believe Sustainable Intensification to be,” she adds.
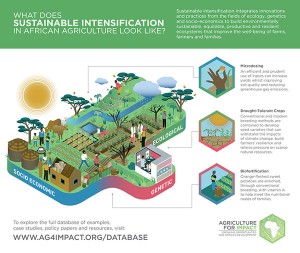
According to Agriculture for Impact, Sustainable Intensification, comprises a combination of approaches from three categories:
- Ecological: environmentally sustainable approaches such as intercropping, integrated pest management and precision farming;
- Genetic: conventional and modern breeding methods for crops and livestock; and
- Socio-economic: creating an enabling environment for farmers to access training, finance, inputs and functioning markets.
Within each category or pillar three selected methods or technologies, with 27 sub-sets and accompanying case studies, illustrate the pros and cons of each method. Technical briefs related to each pillar will be available for download, offering more in-depth analysis.
Access the Sustainable Intensification database at:
Sustainable Intensification approaches covered in database:
Ecological Intensification:
- Precision farming (microdosing, soil testing, seed spacing)
- Building natural capital (conservation agriculture, water conservation, organic agriculture)
- Diversification (multiple cropping, agroforestry, integrated pest management)
Genetic Intensification:
- Conventional breeding (biofortification, hybrids, participatory plant breeding)
- Biotechnology (marker-aided selection, tissue culture, recombinant DNA)
- Livestock breeding (artificial insemination, cross-breeding, embryo transfer)
Socio-economic intensification:
- Creating enabling environments (markets, insurance, finance)
- Building social capital (value chains, institutions, cooperatives)
- Building human capital (education and training, extension, participatory research)
– Ends –
About Agriculture for Impact
Agriculture for Impact (A4I) is an independent advocacy initiative led by Professor Sir Gordon Conway, author of the book One Billion Hungry: Can We Feed the World? A4I aims to enable better European government support for productive, sustainable, equitable and resilient agricultural development in sub-Saharan Africa, focusing in particular on the needs of smallholder farmers. Agriculture for Impact also convenes the Montpellier Panel, a group of European and African experts in the fields of agriculture, trade, ecology and global development. It is based at Imperial College London and is supported through the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. www.ag4impact.org






